matplotlib
matplotlib
| |
创建图片与子图
若不创建实例,一切对象名均使用plt!
导入
| |
层次
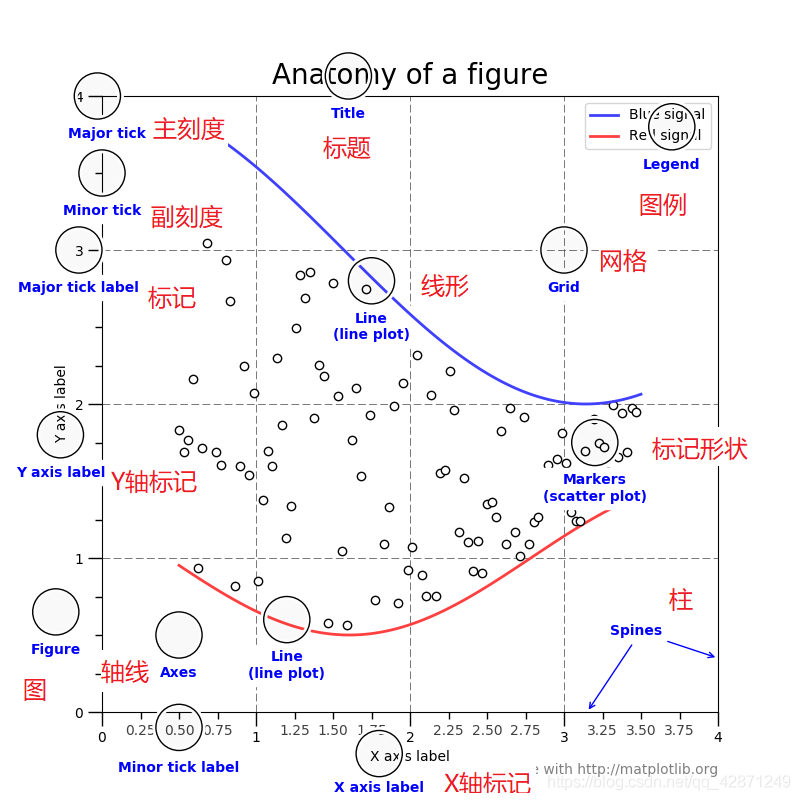
Figure:面板(图),matplotlib 中的所有图像都是位于 figure 对象中,一个图像只能有一个 figure 对象。
Subplot:子图,figure 对象下创建一个或多个 subplot 对象(即 axes)用于绘制图像。
创建图片
| |
plt.figure()返回 figure 实例
一个空白的绘图窗口就会出现
重要参数
num:新图的编号,默认递增
figsize:宽度,高度,以英寸为单位
dpi:分辨率,整数
facecolor:背景颜色
edgecolor:边框颜色
frameon:若为 False,则没有边框
clear:若为 True,如果图的编号已存在则先清除
创建子图
.add_subplot()
| |
fig.add_subplot(nrows, ncols, index)以图片作为对象,返回 Axes 实例
你可以直接在其他空白的子图上调用 Axes 对象的实例方法进行绘图
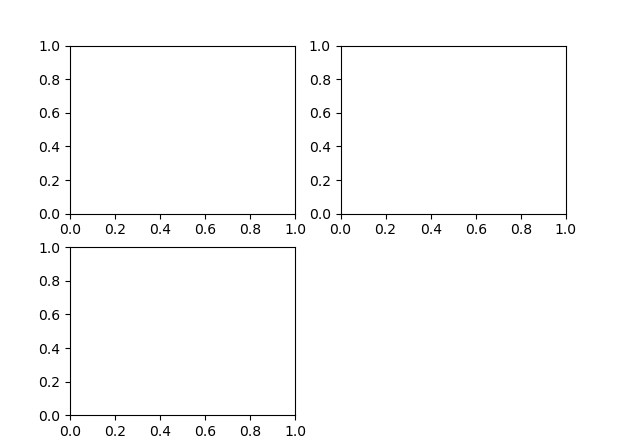
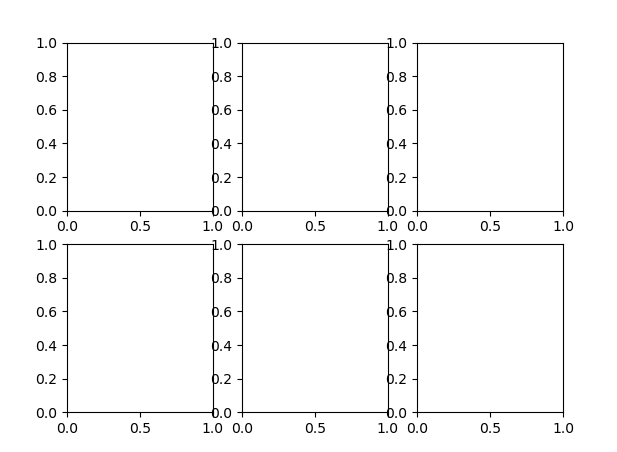
plt.subplots()
使用子图网格创建图片是非常常见的任务,所以 matplotlib 包含了一个便捷方法 plt.subplots,它创建一个新的图片,然后返回包含了已生成子图对象的 NumPy 数组:
| |
API
| |
返回 figure 实例和子图数组
参数
- nrows,ncols:子图的行列数
- sharex, sharey
- 设置为 True 或者 ‘all’ 时,所有子图共享 x 轴或者 y 轴,
- 设置为 False or ‘none’ 时,所有子图的 x,y 轴均为独立,
- 设置为 ‘row’ 时,每一行的子图会共享 x 或者 y 轴,
- 设置为 ‘col’ 时,每一列的子图会共享 x 或者 y 轴。
- squeeze:设置返回的子图对象的数组格式。
- 当为 False 时,不论返回的子图是只有一个还是只有一行,都会用二维数组格式返回他的对象。
- 当为 True 时,如果子图只有一个,则返回的子图对象是标量形式,如果子图有(N×1)或(1×N)个,则返回的子图对象是一维数组,如果是(N×M)则返回二维数组。
- subplot_kw:字典格式,传递给
add_subplot(),用于创建子图 - gridspec_kw:字典格式,传递给
GridSpec的构造函数,用于创建子图所摆放的网格。 - **fig_kw :所有其他关键字参数都传递给
figure()调用。
格式
| |
数组 axes 可以像二维数组那样方便地进行索引,例如,axes[0,1]
调整子图周围的间距
默认情况下,matplotlib 会在子图的外部和子图之间留出一定的间距。这个间距都是相对于图的高度和宽度来指定的,所以如果你通过编程或手动使用 GUI 窗口来调整图的大小,那么图就会自动调整。
可以使用图对象上的plt.subplots_adjust方法更改间距
| |
API
| |
参数
- left, right, bottom, top:子图所在区域的边界
- 当值大于 1.0 的时候子图会超出 figure 的边界从而显示不全;值不大于 1.0 的时候,子图会自动分布在一个矩形区域
- 要保证 left < right, bottom < top,否则会报错
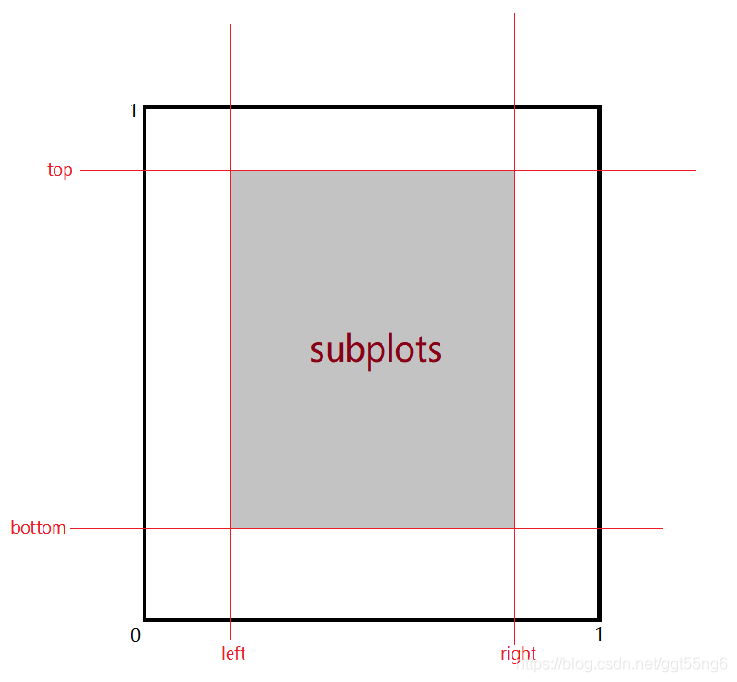
- wspace, hspace:子图之间的横向间距、纵向间距分别与子图平均宽度、平均高度的比值,也就是图片的宽度和高度百分比
修饰
设置标题
设置图片标题
| |
若要直接在 figure 上操作
| |
常用参数
- fontsize:设置字体大小,默认 12,
['xx-small', 'x-small', 'small', ‘medium’, ‘large’, ’x-large’, ‘xx-large’]
- fontweight:设置字体粗细
[‘light’, ‘normal’, ‘medium’, ‘semibold’, ‘bold’, ‘heavy’, ‘black’]
- fontstyle:设置字体类型
[ ‘normal’, ‘italic’, ‘oblique’ ];italic 斜体,oblique 倾斜
- color:设置字体颜色
- verticalalignment:设置水平对齐方式
[ ‘center’ , ‘top’ , ‘bottom’ ,’baseline’]
- horizontalalignment:设置垂直对齐方式
['left', 'right', 'center']
- rotation:旋转角度
[‘vertical’, ‘horizontal’]也可以为数字
- alpha:透明度,参数值 0 至 1 之间
- backgroundcolor:标题背景颜色
- bbox:给标题增加外框
‘boxstyle’:方框外形‘facecolor’:(简写 fc)背景颜色‘edgecolor’:(简写 ec)边框线条颜色‘edgewidth’:边框线条大小
设置子图标题
| |
用 Axe 对象接受此函数
参数见 2.1.1
轴操作
set 方法允许批量设置绘图属性,如
| |
改变轴刻度
| |
若要直接在figure上操作
| |
添加轴标签
添加与刻度对应的标签
| |
添加单一轴标签
| |
参数见 2.1.1
若要直接在figure上操作
| |
设置显示范围
| |
xmin:x 轴上的最小值
xmax:x 轴上的最大值
y 轴亦如是
| |
添加图例
.lengend()自动接受图像的label值,(label值在画图时传入)
| |
常用参数
- loc:设置图列位置,数字代表在第几象限
['best','upper right','upper left', 'lower left','lower right', 'right', 'center left', 'center right', 'lower center','upper center','center']
- fontsize:设置图例字体大小
- int or float or
{‘xx-small’, ‘x-small’, ‘small’, ‘medium’, ‘large’, ‘x-large’, ‘xx-large’}
- int or float or
- 设置图例边框及背景
frameon=False:去掉图例边框edgecolor='blue':设置图例边框颜色facecolor='blue':设置图例背景颜色,若无边框,参数无效
- title:设置图例标题
- markerfirst:如果为 True(默认),则图例标记位于图例标签的左侧
- ncol:设置图例分为 n 列展示
若要直接在 figure 上操作
| |
添加注释
.text()
| |
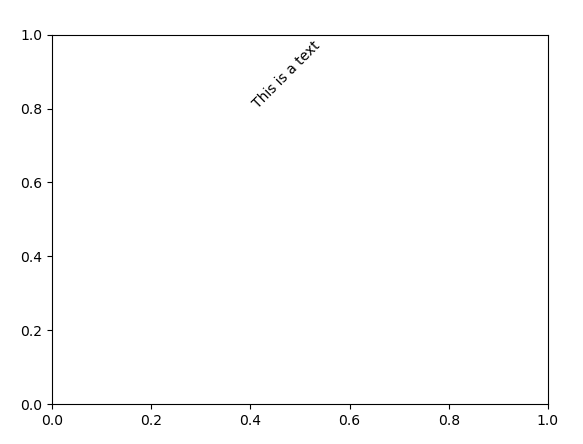
API
| |
参数
- x,y:设置坐标值值
- string:设置说明文字
- 其余详见 2.1.1
.annotate()
| |
API
| |
参数
- string:设置注释文本内容
- xy:设置被注释的坐标点
- xytext:设置注释文字的坐标位置
添加网格
| |
绘制参考线
| |
y或x:水平参考线的出发点
c:参考线的线条颜色
ls:参考线的线条风格
lw:参考线的线条宽度
其他坐标轴设置
| |
参数
- ‘equal’:x,y 轴刻度等长
- ‘off’:关闭坐标轴
- [a, b, c, d]:设置 x 轴的范围为[a, b],y 轴的范围为[c, d]
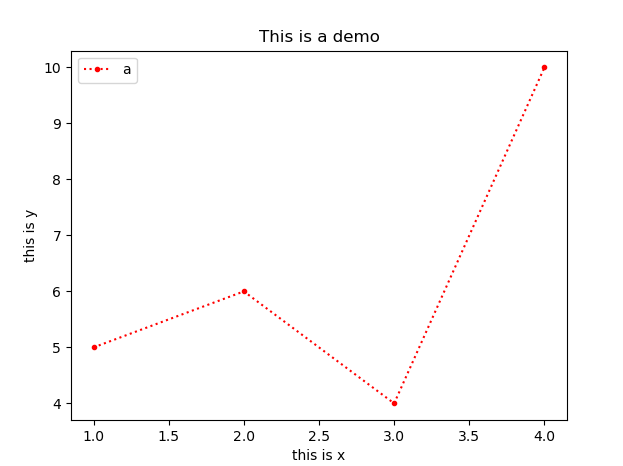
绘图
点图,线图
| |
API
| |
参数
x,y:数据,x 可选
fmt:定义基本属性
fmt = '[color][marker][line]'**kwargs
label
linestyle (ls)
{''-', '--', '-.', ':', ' '}
linewidth (lw):线宽
color
- 可以用缩写、RGB、灰度字符串
character color ‘b’ blue ‘g’ green ‘r’ red ‘c’ cyan ‘m’ magenta ‘y’ yellow ‘k’ black ‘w’ white marker
character description '.'point marker ','pixel marker 'o'circle marker 'v'triangle_down marker '^'triangle_up marker '<'triangle_left marker '>'triangle_right marker '1'tri_down marker '2'tri_up marker '3'tri_left marker '4'tri_right marker 's'square marker 'p'pentagon marker '*'star marker 'h'hexagon1 marker 'H'hexagon2 marker '+'plus marker 'x'x marker 'D'diamond marker 'd'thin_diamond marker `' ‘` '_'hline marker alpha:透明值,接受 0~1 之间的浮点数
例
| |
散点图
| |
| |
气泡图
加入了第三个值 s 可以理解成普通散点,画的是二维,泡泡图体现了 Z 的大小
s:散点标记的大小
c:散点标记的颜色
cmap:将浮点数映射成颜色的颜色映射率
| |
柱状图
| |
x:标示在 x 轴上的定性数据的类别
y:每种定性数据的类别的数量
align:每个柱状图的位置对齐方式
{'center', 'edge'}, optional, default: 'center'}
| |
| |
直方图
直方图用于表明数据分布情况,横轴是数据,纵轴是出现的次数(也就是频数)
| |
x:在 x 轴上绘制箱体的定量数据输入值
重要参数
x : arrays(一个或多个),在 x 轴上绘制箱体的定量数据输入值
range : 设置显示范围(tuple or None, optional)
bins:x 轴的分段数,默认为 10
histtype : 选择展示的类型,默认为 bar
{‘bar’, ‘barstacked’, ‘step’, ‘stepfilled’}
align : 对齐方式
{‘left’, ‘mid’, ‘right’}
orientation : 直方图方向
{‘horizontal’, ‘vertical’}
log : boolean,log 刻度
color:颜色设置
label:刻度标签
例
| |
饼图
饼图自动根据数据的百分比画饼
| |
重要参数
x: 定性数据的不同类别的百分比
explode:指定饼图某些部分的突出显示,即呈现爆炸式,传入元组,每个数据分别为 0-1 的浮点,表示分离的程度
1 2sizes = [15, 30, 45, 10] explode = (0, 1, 0, 0)
labels:为饼图添加标签说明,类似于图例说明
colors:指定饼图的填充色
autopct:设置百分比格式,如’%.1f%%‘为保留一位小数
shadow:是否添加饼图的阴影效果
pctdistance:设置百分比标签与圆心的距离
labeldistance:设置各扇形标签(图例)与圆心的距离;
startangle:设置饼图的初始摆放角度, 180 为水平;
radius:设置饼图的半径大小;
wedgeprops:设置饼图内外边界的属性,如边界线的粗细、颜色等, 如
wedgeprops = {'linewidth': 1.5, 'edgecolor':'green'}textprops:设置饼图中文本的属性,如字体大小、颜色等;
center:指定饼图的中心点位置,默认为原点
例
| |
箱型图
| |
- x:数据
- vert:方向
| |
棉棒图
绘制离散有序数据
| |
x:制定棉棒的 x 轴基线上的位置
y:绘制棉棒的长度
linefmt:棉棒的样式
markerfmt*:棉棒末端的样式
basefmt*:指定基线的样式
| |
三维图
| |
其他
保存
| |
参数
- path:文件路径
- dpi:分辨率
- facelolor,edgecolor:子图之外的图形背景颜色,默认为
‘w’ - format:文件格式
'png','pdf','svg','ps',''eps'......
- bbox_inches:要保存的图片范围,若传递
'tight',会去除图片周围空白部分
解决中文乱码问题
| |